728x90
The Bad Guys Can Put Malware into Your Host Via the Internet
- Once malware infects our device it can do all kinds of devious things, including deleting our files and installing spyware that collects our private information
- such as social security numbers, passwords, and keystrokes, and then sends this (over the Internet, of course!) back to the bad guys.
- Viruses are malware that require some form of user interaction to infect the user’s device.
- Worms are malware that can enter a device without any explicit user interaction
The Bad Guys Can Attack Servers and Network Infrastructure
- Another broad class of security threats are known as denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- Most Internet DoS attacks fall into one of three categories:
- 1) Vulnerability attack : This involves sending a few well-crafted messages to a vulnerable application or operating system running on a targeted host.
- 2) Bandwidth flooding : The attacker sends a deluge of packets to the targeted host—so many packets that the target’s access link becomes clogged, preventing legitimate packets from reaching the server.
- 3) Connection flooding : The attacker establishes a large number of half-open or fully open TCP connections at the target host
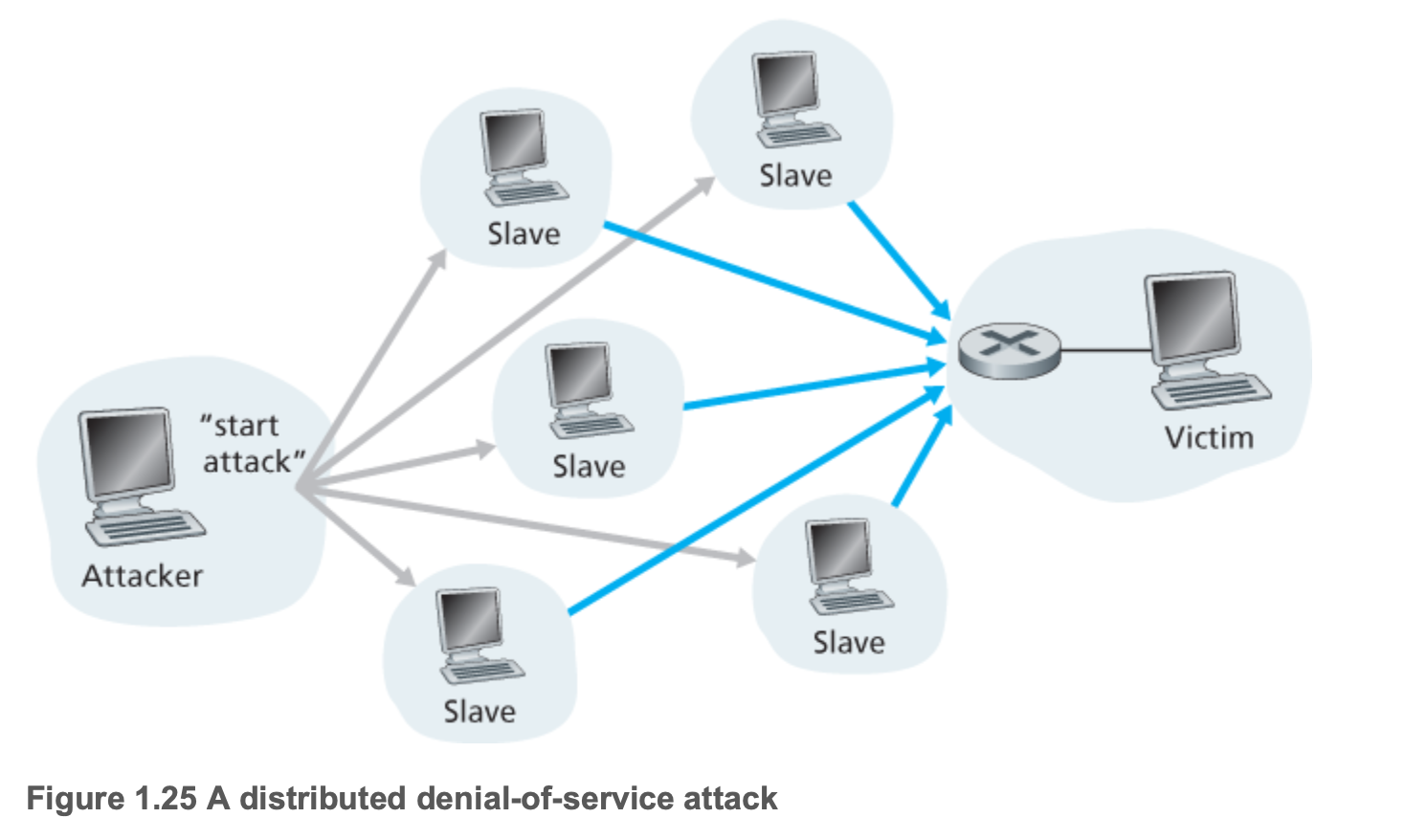
- In a distributed DoS (DDoS) attack, illustrated in Figure 1.25, the attacker controls multiple sources and has each source blast traffic at the target.
The Bad Guys Can Sniff Packets
- These packets can contain all kinds of sensitive information, including passwords, social security numbers, trade secrets, and private personal messages
- A passive receiver that records a copy of every packet that flies by is called a packet sniffer.
- a bad guy who gains access to an institution’s access router or access link to the Internet may be able to plant a sniffer that makes a copy of every packet going to/from the organization.
- Sniffed packets can then be analyzed offline for sensitive information.
- Packet-sniffing software is freely available at various Web sites and as commercial products.
The Bad Guys Can Masquerade as Someone You Trust
- The ability to inject packets into the Internet with a false source address is known as IP spoofing, and is but one of many ways in which one user can masquerade as another user.
- To solve this problem, we will need end-point authentication, that is, a mechanism that will allow us to determine with certainty if a message originates from where we think it does
728x90
'네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2.1.3 Transport Services Available to Applications (0) | 2023.07.18 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 2 Application Layer (0) | 2023.07.15 |
| Protocol Layering (0) | 2023.07.13 |
| 1.4.4 Throughput in Computer Networks (0) | 2023.06.20 |
| 1.4 Delay, Loss, and Throughput in Packet-Switched Networks (0) | 2023.06.11 |




댓글