To send a message from a source end system to a destination end
system, the source breaks long messages into smaller chunks of data known as packets.
Between
source and destination, each packet travels through communication links and packet switches (for
which there are two predominant types, routers and link-layer switches)
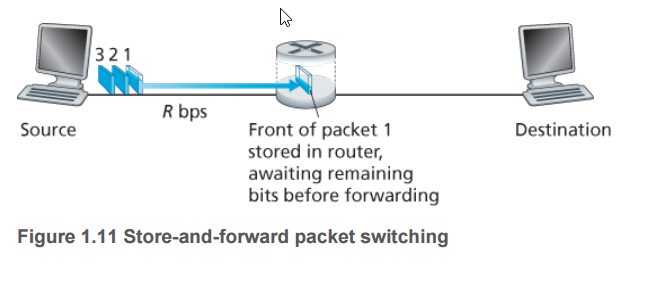
Most packet switches use store-and-forward transmission at the inputs to the links. Store-and-forward
transmission means that the packet switch must receive the entire packet before it can begin to transmit
the first bit of the packet onto the outbound link
<Queuing Delays and Packet Loss>
Each packet switch has multiple links attached to it. For each attached link, the packet switch has an
output buffer (also called an output queue), which stores packets that the router is about to send into
that link.
Thus, in addition to the store-and-forward delays, packets suffer output
buffer queuing delays. These delays are variable and depend on the level of congestion in the network.
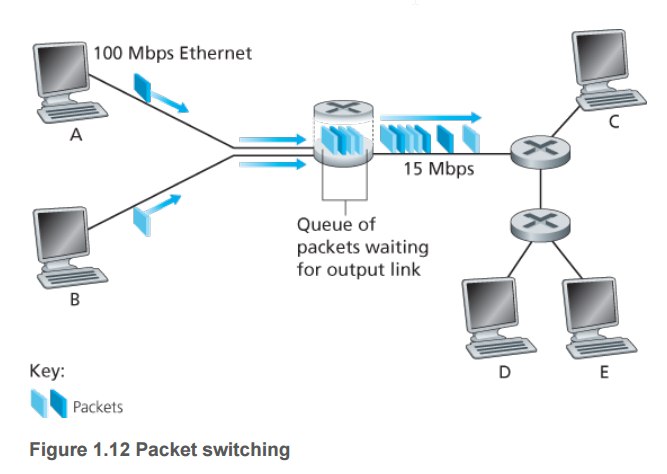
The width of a slab represents the number of bits in the packet
In this figure, all packets have the same width and hence the same length.
<Forwarding Tables and Routing Protocols>
But how does the router determine which link it should forward the packet onto? Packet forwarding is actually done in different
ways in different types of computer networks
In the Internet, every end system has an address called an IP address
When a source end system
wants to send a packet to a destination end system, the source includes the destination’s IP address in
the packet’s header.
As with postal addresses, this address has a hierarchical structure.
each router has a forwarding table that
maps destination addresses (or portions of the destination addresses) to that router’s outbound links.
(a forwarding table => 네이게이션 테이블이라 생각하면 목적지까지 어디 고속도로를 타야되는지 이런식으로 알수 있는 테이블을 말한다.)
When a packet arrives at a router, the router examines the address and searches its forwarding table,
using this destination address, to find the appropriate outbound link. The router then directs the packet
to this outbound link.
this statement begs yet another question: How do forwarding tables get set?
we’ll note now that the Internet has a number of special routing protocols that are used
to automatically set the forwarding tables.
A routing protocol may, for example, determine the shortest
path from each router to each destination and use the shortest path results to configure the forwarding
tables in the routers.
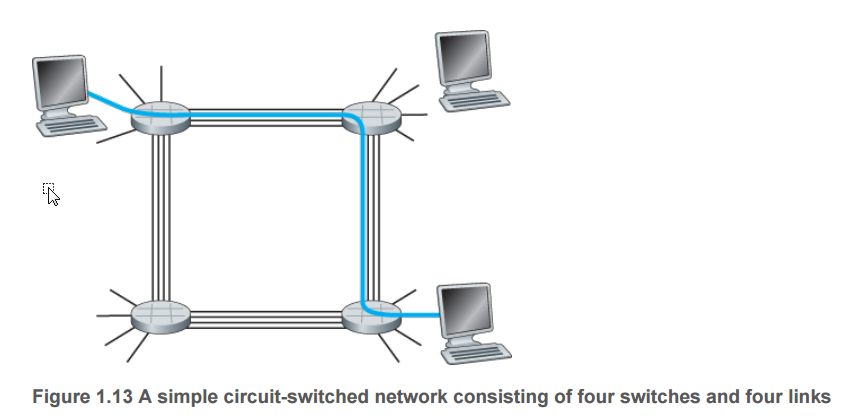
<1.3.2 Circuit Switching>
There are two fundamental approaches to moving data through a network of links and switches: circuit
switching and packet switching
s. In packet-switched networks, these resources are not reserved; a
session’s messages use the resources on demand and, as a consequence, may have to wait (that is,
queue) for access to a communication link.
the sender can send the information, the network must establish a connection between the
sender and the receiver
In the jargon of telephony, this connection is called a circuit.
'네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 1.5 Protocol Layers and Their Service Models (0) | 2025.04.22 |
|---|---|
| 1.2 The Network Edge (0) | 2025.04.16 |
| 1.1 what is the internet? (0) | 2025.04.16 |
| 내부 네트워크 외부 네트워크 (0) | 2025.03.15 |
| 스위치와 브리지 차이 (0) | 2024.01.18 |


댓글